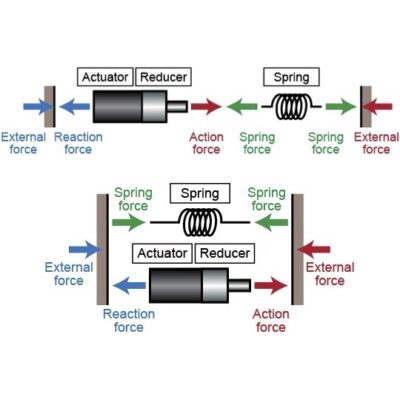
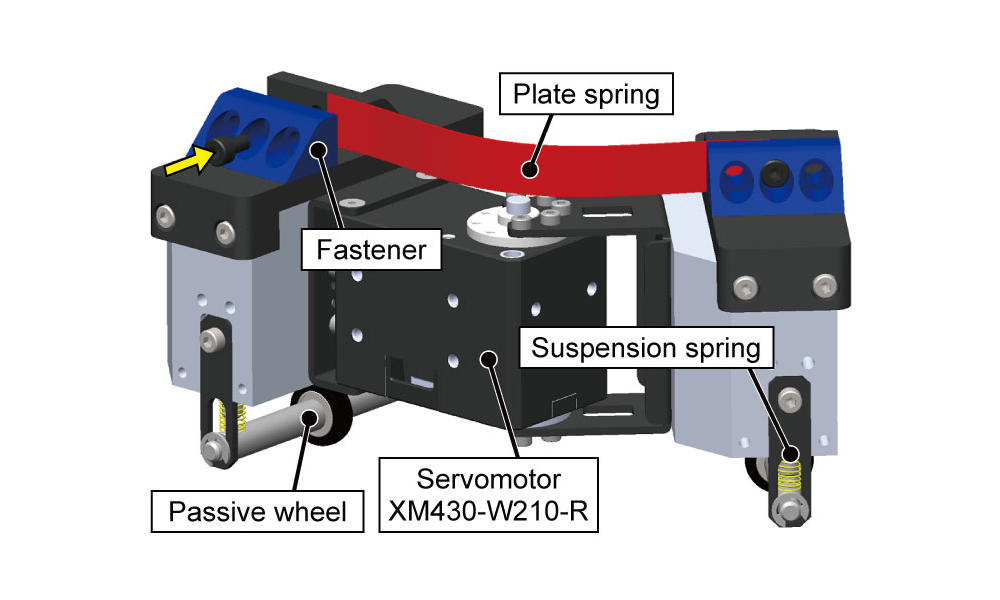
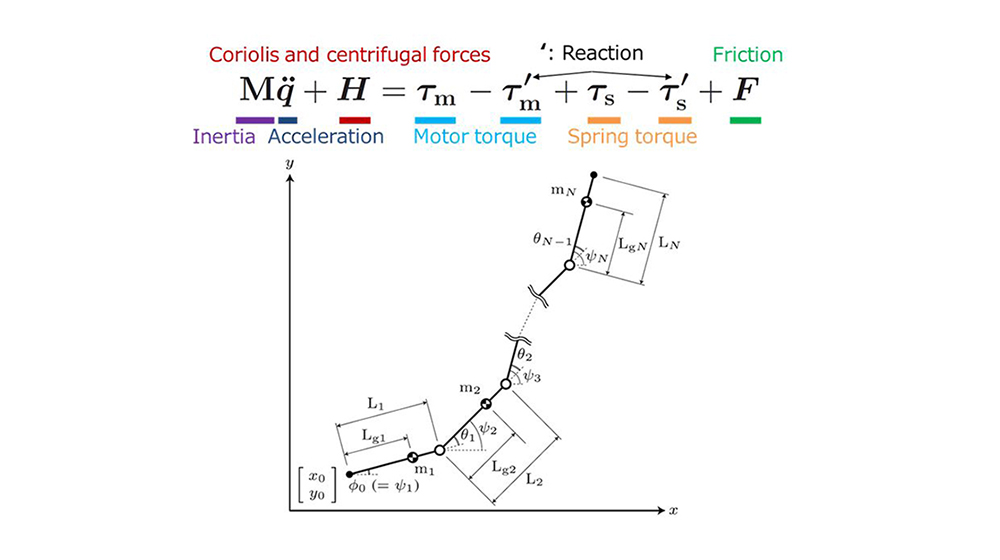
Elastic bodies such as springs vibrate when they are bounced. In this state, elastic energy and kinetic energy are converted, and if there is no loss due to energy dissipation, the body will continue to vibrate forever (single vibration). On the other hand, robots also need periodic motions such as vibration sometimes. For example, walking motions with legs, pick-and-place movements of manipulators, and serpentine locomotion of snake-like robots. If these motions can be harmonized (resonated) with the vibrations of elastic materials, energy efficiency can be significantly improved. Such a method is called Parallel Elastic Actuator (PEA), and has already been introduced here.


※本成果は,立命館大学生物知能機械学研究室やウォータールー大学Mechanical Systems & Control Laboratoryとの共同研究の結果,生まれたものです.また,科学研究費助成事業(若手研究)「板バネとDDモータによる周期運動のための高効率小型並列弾性アクチュエータの研究」19K14949の支援を受けました.
Related works
- Atsushi Kakogawa, Taihei Kawabata, and Shugen Ma, Plate-springed Parallel Elastic Actuator for Efficient Snake Robot Movement, IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, Vol. 26, Iss. 6, pp. 3051-3063, 2021
- Atsushi Kakogawa, Taihei Kawabata, and Shugen Ma, Plate Springed Parallel Elastic Actuators for Efficient Movement of a Planar Snake Robot, Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM 2019), pp. 235-240, 2019
- 加古川篤,川端泰平,馬書根,並列弾性アクチュエータを用いたヘビ型ロボットの低速運動時におけるエネルギー消費抑制,システム制御情報学会論文誌,32巻,6号,pp. 227-233, 2019
- 加古川篤,馬書根,並列弾性アクチュエータを用いた高効率2次元ヘビ型ロボットの剛性設計,第62回システム制御情報学会研究発表講演会 (SCI’18),2018
- Atsushi Kakogawa, Soo Jeon, and Shugen Ma, Stiffness Design of a Resonance-based Planar Snake Robot with Parallel Elastic Actuators, IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), Vol. 3, Iss. 2, pp. 1284-1291, 2018
Previous studies that served as references for this study
- S. Hirose, Biologically Inspired Robots, London, U.K.: Oxford University Press, 1993
- D. W. Robinson, J. E. Pratt, D. J. Paluska and G. A. Pratt, Series elastic actuator development for a biomimetic walking robot, Proc. IEEE/ASME Int. Conf. Adv. Intell. Mechatron., pp. 561-568, Sep. 1999
- J. Hurst and A. Rizzi, Series compliance for an efficient running gait, IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag., vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 42-51, Sep. 2008
- M. Uemura, K. Kanaoka, and S. Kawamura, A new control method utilizing stiffness adjustment of mechanical elastic elements for serial link systems, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., pp. 1437–1442, 2007
- M. Uemura and S. Kawamura, Resonance-based motion control method for multi-joint robot through combining stiffness adaptation and iterative learning control, Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom., pp. 1543-1548, 2009
- M. Uemura,, H. Goya and S. Kawamura, Motion control with stiffness adaptation for torque minimization in multijoint robots, IEEE Trans. Robot., vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 352-364, 2014
- K. Ono, T. Furuichi and and R. Takahashi, Self-excited walking of a biped mechanism with feet, Int., J. Robot. Res., vol. 20, no. 12, pp. 953-966, 2001
- J. Ute and K. Ono, Fast and efficient locomotion of a snake robot based on self-excitation principle, Proc. 7th Int. Workshop Adv. Motion Control, pp. 532–539, 2002
- D. Efimov, A. Fradkov and and T. Iwasaki, On finite time resonance entrainment in multi-DOF systems, Proc. Amer. Control Conf., pp. 1035-1039, 2012