Actuation Laboratory at Ritsumeikan University conducts research and development of socially useful field robots and service robots based on mechanism and control technology. Join us in creating exciting new robots!
We are working on research and development of field robots and service robots under the theme of -How can we successfully generate the motion of objects with mass and shape and the forces acting on them, and how can we utilize them for society?- This is true for cases such as when a robotic arm moves an object to a target location with high speed and repeatability, or when a robot itself reaches a location that is inaccessible to humans. We are studying the actuation of robots, and other physical objects to give them energy, convert them into motion, and manipulate them from the viewpoint of mechanism and control.
Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs) and Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) are well known in the f
Numerous efforts to reduce friction in the sliding parts of reduction gears have been reported to e
Elastic bodies such as springs vibrate when they are bounced. In this state, elastic energy and kin
The maintenance of pipeline used for gas, water, sewage, and air conditioning is one of the major c
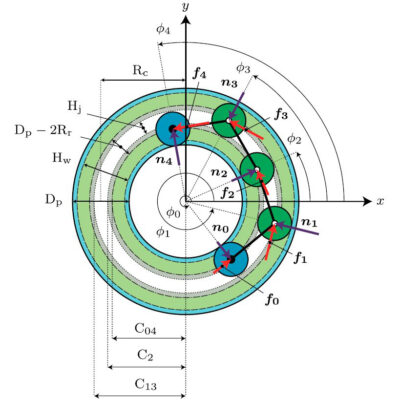
Dynamic analysis that is applied to the design and control of robot mechanisms. Statics analysis, which deals only with the balance of forces and moments, and dynamics analysis, which includes kinematic parameters such as velocity and acceleration, are used according to the application.
Dynamic analysis that is applied to the design and control of robot mechanisms. Statics analysis, which deals only with the balance of forces and moments, and dynamics analysis, which includes kinematic parameters such as velocity and acceleration, are used according to the application.
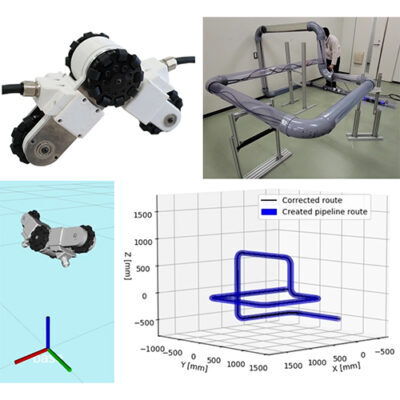
Technologies which are used to recognize the robot's surrounding environment by making full use of various external (camera, laser sensor, etc.) and internal (encoder, acceleration sensor, gyro sensor, etc.) sensors.
Technologies which are used to recognize the robot's surrounding environment by making full use of various external (camera, laser sensor, etc.) and internal (encoder, acceleration sensor, gyro sensor, etc.) sensors.
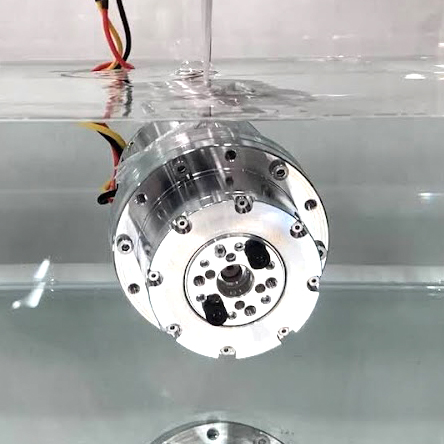
Geared motors that do not use any lubricating oil or waterproof seals (O-rings or V-rings). To enable submersion, gears made of polymeric materials and rust-proof motors are used.
Geared motors that do not use any lubricating oil or waterproof seals (O-rings or V-rings). To enable submersion, gears made of polymeric materials and rust-proof motors are used.
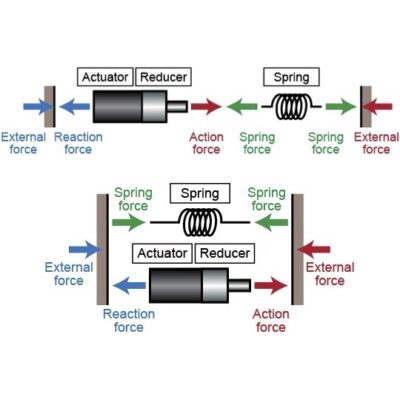
A method of combining an elastic element with a geared motor. There are two types of elastic actuator: series elastic actuator, in which elastic elements are arranged in series with the output, and parallel elastic actuator, in which elastic elements are arranged in parallel.
A method of combining an elastic element with a geared motor. There are two types of elastic actuator: series elastic actuator, in which elastic elements are arranged in series with the output, and parallel elastic actuator, in which elastic elements are arranged in parallel.