ガス,上下水道,空調などに用いられる配管設備のメンテナンスは都市社会において人類が直面する大きな課題の一つとなっています.特に,地下や高層ビルに設置されたものについては,外から点検することが困難なため,老朽化したパイプの特定に莫大なコストと時間を要します.
一般的な配管検査において,これまで市販の工業用内視鏡が用いられてきました.しかし,多くの配管にはベンドやエルボーと呼ばれるたくさんの曲がりやチーズと呼ばれるT字の分岐が含まれています.従来の押し込み式カメラの場合,このような経路ではせいぜい2~3箇所の曲がりしか通過できませんでした.そのため,複数の曲がりやT字分岐を通過可能な自走式ロボットによる配管内検査に期待が寄せられています.
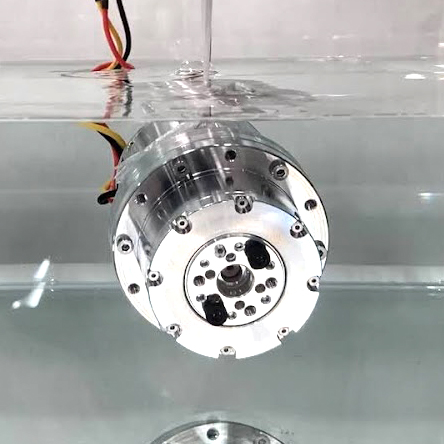
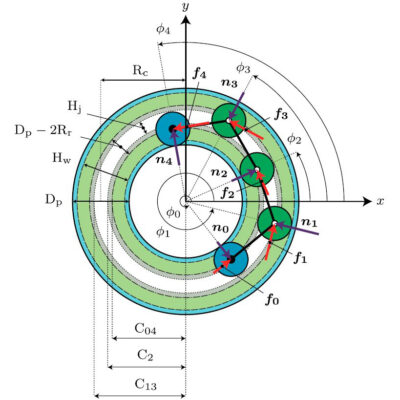
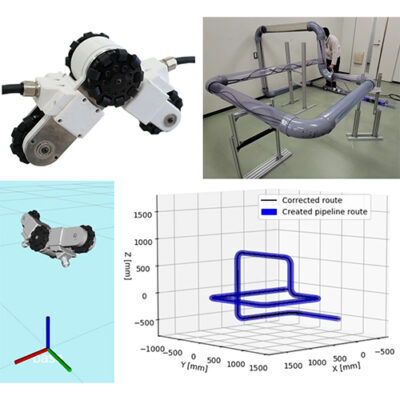
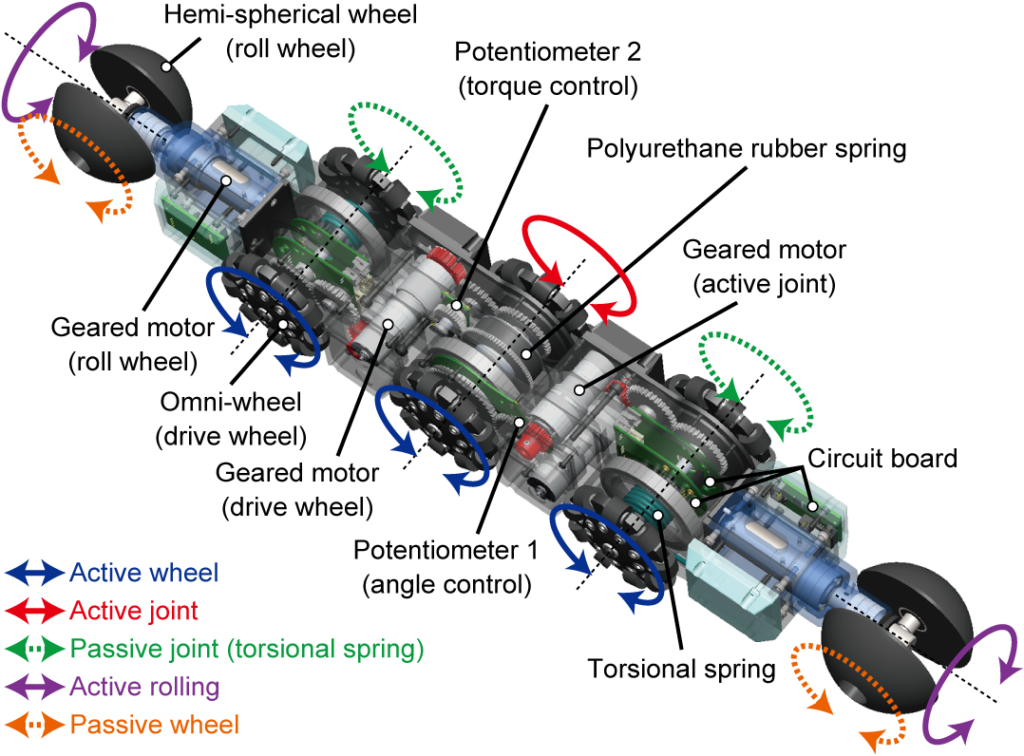
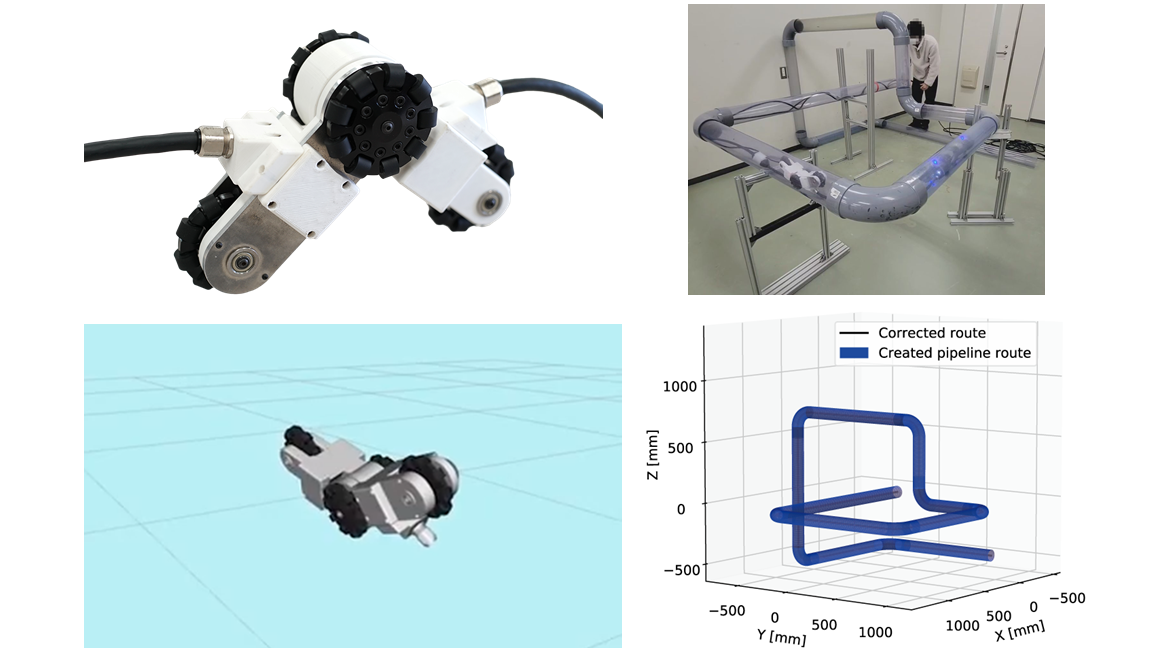
本研究で開発したロボット「AIRo」は3つの関節と前進後退を行うための3つのオムニホイール,ロール回転(進行方向周りに転がる動作)するための2つの球状車輪で構成されています.車軸と関節軸が同一直線上にあるため,機能性を落とさずに大幅な小型化が可能で,適応内径の範囲も大きくすることができます.
初期に開発したAIRo-1〜2では,全ての関節がねじりコイルばねによって受動的に曲げられるよう設計されていましたが,AIRo-5では,中央関節のみにモータや減速機,トルクセンサが内蔵され,角度制御とトルク制御が両方可能になりました.
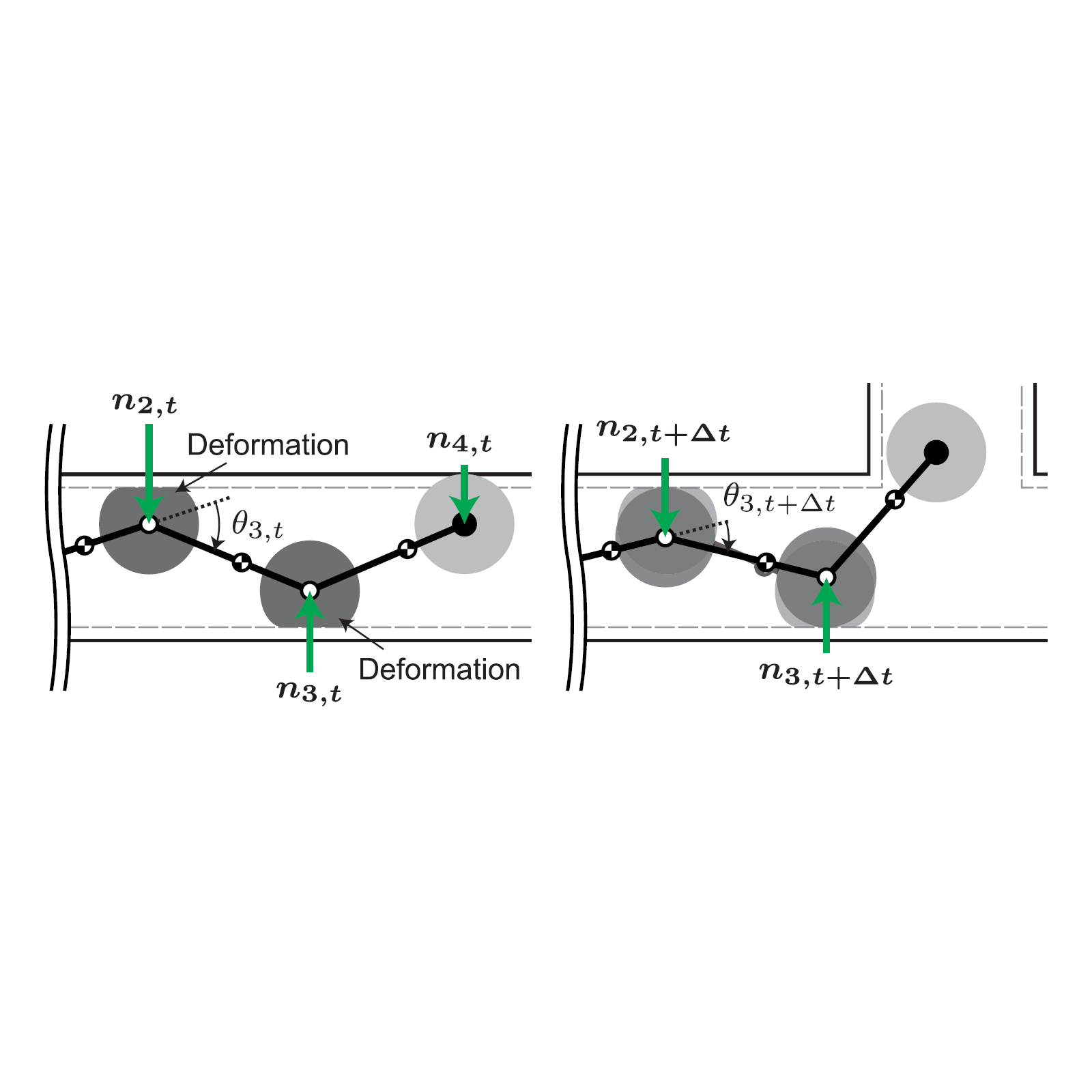
最新機であるAIRo-5.2では,曲がりの通過を関節トルク制御のみで実現し,T字分岐の通過については関節角度とトルクの両方の制御を切り替えることで実現します.特に,T字管の走行については中央関節角度を移動距離に対して余弦波(cos)の軌道で制御すれば上手く通過できることが明らかとなりました.
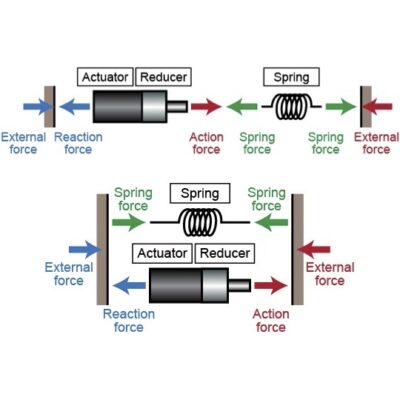
また,市販のトルクセンサは大きく,衝撃力などに対して弱いため,独自に開発したポリウレタン式の直列弾性アクチュエータ(通称:SEA)を搭載しています.これにより,内径100mm以下の限られた空間でトルク制御が可能となっただけでなく,耐衝撃性も向上しました.
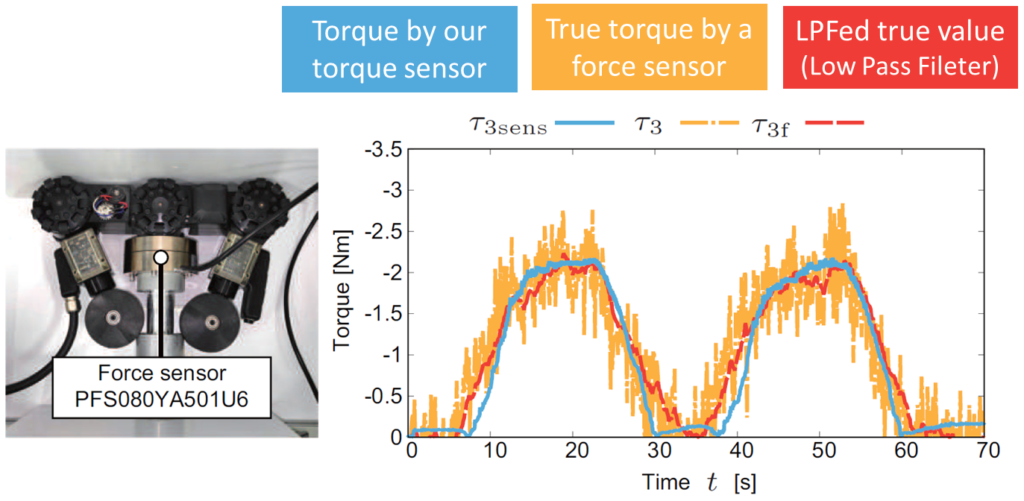
何度か改良を行った結果,AIRo-5.2では,15本以上の曲がりと重力方向の異なる10種類のT字分岐管を滑らかに通過することができ,25kgf(約250N)以上の牽引力を発生可能となりました.実験では,内径4インチ(約100mm)の水平・垂直の合計19個の曲がりを含むパイプコースを約26m走行することに成功しました.これほど経路が曲がりくねった配管を奥まで進めるロボットは世界でも他に類を見ません.
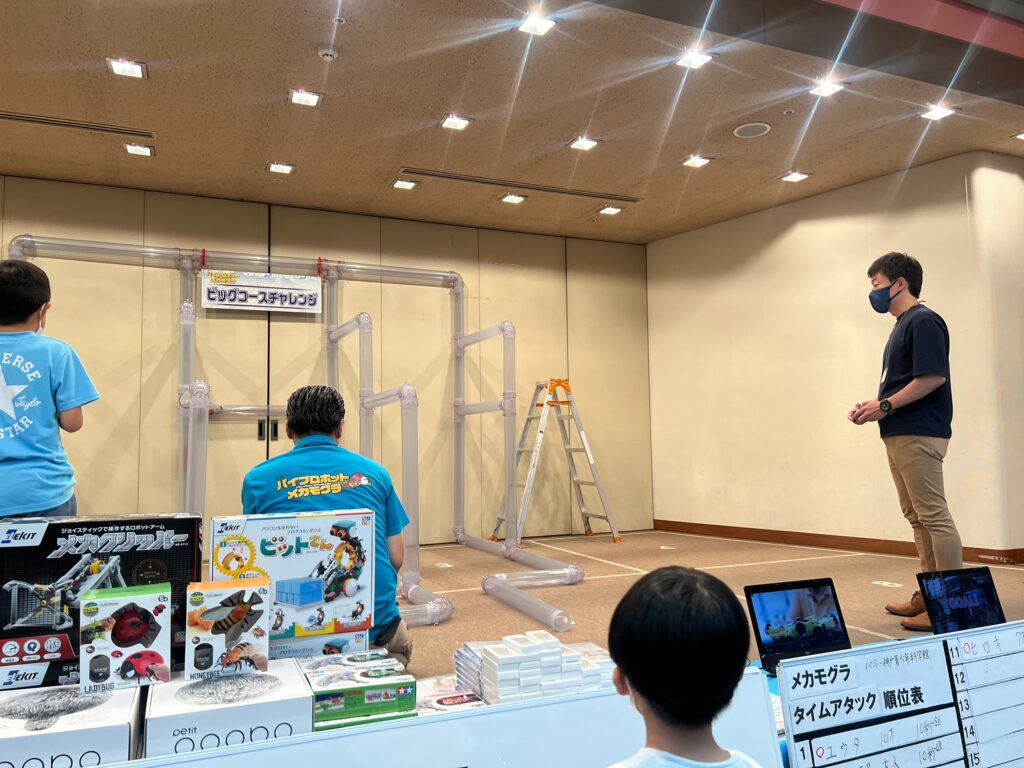
これらの基礎研究から生まれた成果は,プラントやガス管,排水管の点検を目的に複数社の民間企業へも技術移転されており,高い評価を得ています.教育用おもちゃ「メカモグラ」としても商品化され,毎月全国の科学館で開催されているパイプロボコンにて子供達に親しまれています.
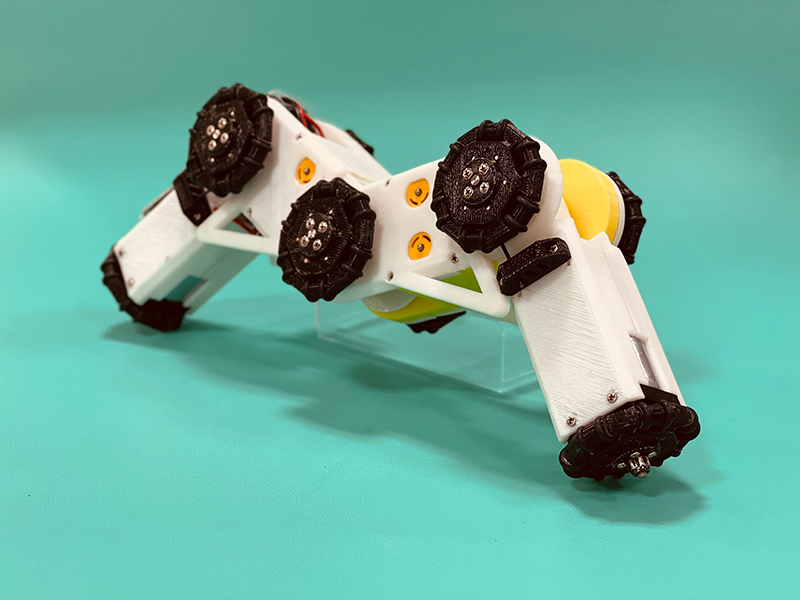





なお,AIRoという名前は連結車輪型配管内検査ロボットArticulated wheeled In-pipe inspection Robotの頭文字や日本語で狭い経路のことを「隘路(あいろ)」ということから由来しています.
本研究に関連する要素研究
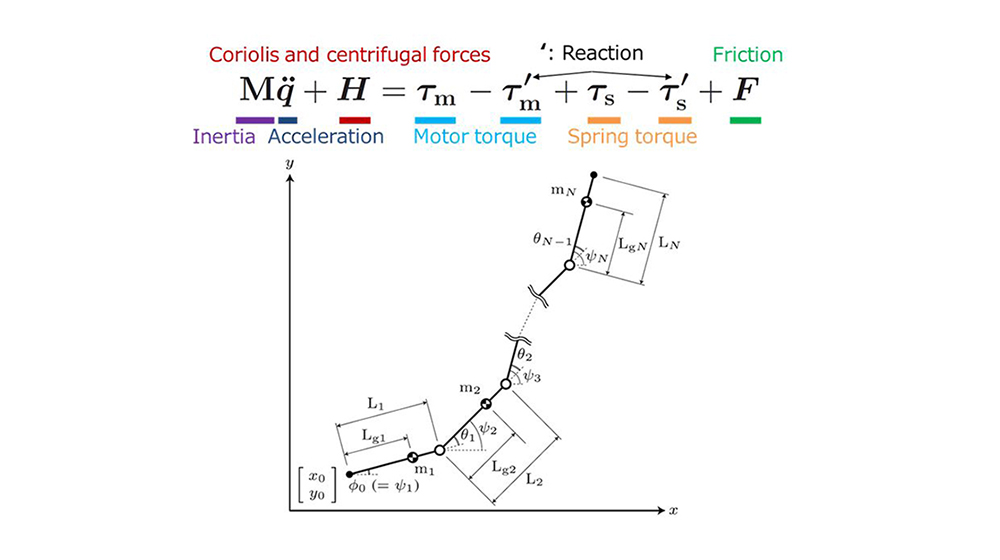
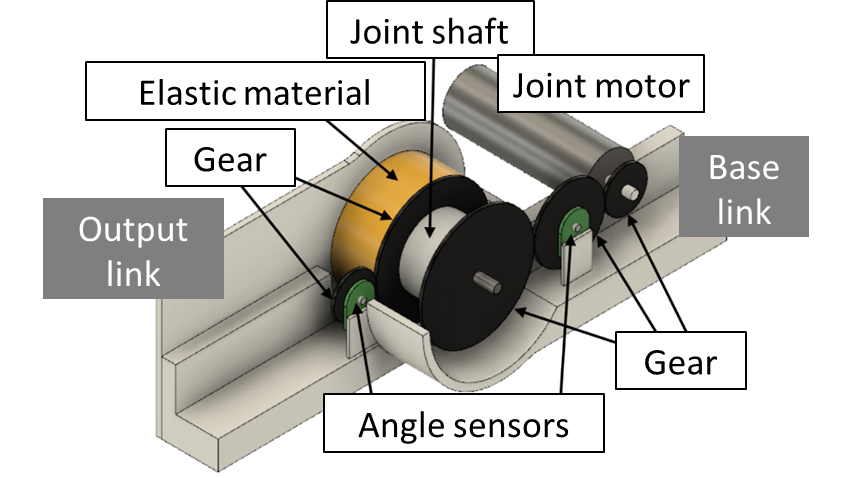
※本成果は,立命館大学生物知能機械学研究室との共同研究の結果,生まれたものです.また,国土交通省・下水道技術研究開発(GAIA プロジェクト)「トルク感知可能な能動関節機構およびSLAM技術を搭載した防水ヘビ型管路検査移動ロボットの開発」の支援を受けました.
関連文献
- Atsushi Kakogawa, Kenya Murata, and Shugen Ma, Automatic T-branch Travel of an Articulated Wheeled In-pipe Inspection Robot Using Joint Angle Response to Environmental Changes, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, Vo. 70, Iss. 7, pp. 7041-7050, 2023
- Atsushi Kakogawa, Kenya Murata, and Shugen Ma, Vertical Bend and T-branch Travels of an Articulated Wheeled In-pipe Inspection Robot by Combining Its Joint Angle and Torque Controls, Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2022), pp. 13254-13259, 2022
- 村田憲哉,加古川篤,馬書根,1自由度能動関節のみを用いた連結車輪型管内移動ロボットのT字管走行 ―第2 報:角度センサの配置による関節角度およびトルクの計測性能の比較―,日本機械学会ロボティクス・メカトロニクス講演会 2022,2P1-M09,2022
- Atsushi Kakogawa, Yutaro Kushitani, and Shugen Ma, Automatic T-branch Travel of a Multi-link In-pipe Inspection Robot based on Joint Torque Value, 5th International Symposium on Swarm Behavior and Bio-Inspired Robotics (SWARM 2022), 2022
- Atsushi Kakogawa and Shugen Ma, A Multi-link In-pipe Inspection Robot Composed of Active and Passive Compliant Joints, Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2020), pp. 6472-6478, 2020
- 櫛谷侑太郎,加古川篤,馬書根,1自由度能動関節のみを用いた連結車輪型管内移動ロボットのT字管走行,日本機械学会ロボティクス・メカトロニクス講演会 2020,2P1-L08,2020
- 小川恭平,加古川篤,馬書根,川村貞夫,ロボット用せん断支持型高分子弾性要素の機械特性,日本機械学会ロボティクス・メカトロニクス講演会 2020,2P1-L07,2020
- Atsushi Kakogawa and Shugen Ma, An In-pipe Inspection Module with an Omnidirectional Bent-pipe Self-adaptation Mechanism using a Joint Torque Control, Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2019), pp. 4347-4352, 2019
- Atsushi Kakogawa and Shugen Ma, A Differential Elastic Joint for Multi-Linked Pipeline Inspection Robots, Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS 2018), pp. 949-954, 2018
本研究の参考となった先行研究
- G. C. Vradis and W. Leary, Development of an Inspection Platform and a Suite of Sensors for Assessing Corrosion a Mechanical Damage on Unpiggable Transmission Mains, Technical Report of NGA and Foster-Miller, 2004
- E. Dertien, S. Stramigioli, and K. Pulles, Development of an Inspection Robot for Small Diameter Gas Distribution Mains, in Proc. the IEEE Int. Conf. Robotics and Automation, pp. 5044-5049, 2011
- P. Debenest, M. Guarnieri, and S. Hirose, PipeTron Series – Robots for Pipe Inspection, in Proc. of the 3rd Int. Conf. Applied Robotics for the Power Industry, pp.1-6, 2014
- K. Tadakuma, Tetrahedral Mobile Robot with Novel Ball Shape Wheel, in Proc. the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS Int. Conf. Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp. 946-952, 2006
- K. Tadakuma, R. Tadakuma, and J. Berengeres, Development of Holonomic Omnidirectional Vehicle with “Omni-Ball”: Spherical Wheels, in Proc. the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 33-39, 2007
- D. Rollinson, S. Ford, B. Brown, and H. Choset, Design and Modeling of a Series Elastic Element for Snake Robots, in Proc. the ASME Dynamic Systems and Control Conference, pp. 1-5, 2013
- D. Rollinson, Y. Bilgen, B. Brown, F. Enner, S. Ford, C. Layton, J. Rembisz, M. Schwerin, A. Willig, P. Velagapudi and H. Choset, Design and Architecture of a Series Elastic Snake Robot, in Proc. the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 4630-4636, 2014